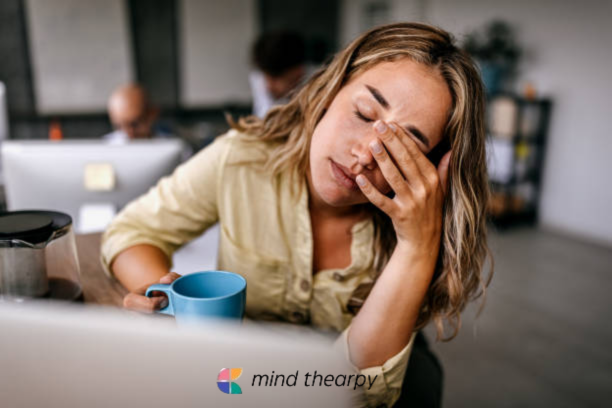
Stress is a universal experience that affects individuals in different ways. It is a natural reaction to tough situations. However, if not managed, it can seriously harm mental and physical health. In this comprehensive guide, we explore what stress is in psychology, its causes, types, and expert-backed management strategies.
What Is Stress in Psychology?
In psychology, stress is defined as the body’s reaction to demands, pressures, or threats. The American Psychological Association (APA) describes stress as “a physiological and psychological response to external or internal stressors.”
The stress response is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which triggers the “fight or flight” reaction. Chronic stress can harm your thinking, emotions, and physical health. It raises the risk of anxiety, depression, and heart disease.
4 Types of Stress
Psychologists classify stress into four primary types:

1. Acute Stress
This is the most common type of stress, characterized by a short-term response to immediate challenges. Examples include:
- Preparing for an important presentation
- Facing a sudden deadline
- Encountering an argument with a friend or colleague
Acute stress usually goes away when the situation is resolved. However, having it often can cause headaches, muscle tension, and anxiety.
2. Episodic Acute Stress
This type of stress occurs in individuals who frequently experience acute stress. People with high-pressure jobs or chaotic lifestyles often suffer from episodic acute stress. Symptoms include:
- Persistent anxiety
- Irritability
- High blood pressure
- Digestive issues
3. Chronic Stress
Chronic stress builds up over time. It often comes from long-term issues like money problems, bad relationships, or work pressure. It can have serious health consequences, including:
- Weakened immune system
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety
4. Traumatic Stress
This type of stress is related to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It happens after facing life-threatening events, like accidents, abuse, or combat. It can lead to severe emotional distress, flashbacks, and difficulty functioning in daily life.
Causes of Stress
Various factors contribute to stress, and understanding them is crucial for effective management. Here are some of the most common causes of stress:
1. Work-Related Stress
- High workload and unrealistic deadlines
- Job insecurity
- Conflicts with colleagues or management
- Lack of work-life balance
2. Financial Stress
- Debt and economic instability
- Rising cost of living
- Unemployment or job loss
3. Relationship Stress
- Family disputes and conflicts
- Marital or romantic relationship issues
- Lack of emotional support
4. Health-Related Stress
- Chronic illnesses
- Diagnosed mental health disorders
- Caregiving responsibilities
5. Environmental Stressors
- Noise pollution
- Crowded spaces
- Natural disasters or global crises
How to Manage and Reduce Stress Effectively
Managing stress requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, psychological techniques, and professional interventions. Below are expert-backed strategies for stress management:
1. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness meditation helps individuals stay present and reduce emotional reactivity. Studies suggest that mindfulness reduces cortisol levels, the hormone responsible for stress.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to combat stress. Activities like yoga, running, or strength training release endorphins, which act as natural mood boosters.
3. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
- Journaling to express emotions
- Engaging in hobbies such as painting or music
- Deep breathing exercises such as the 4-7-8 technique
4. Improve Sleep Quality
Poor sleep exacerbates stress, making it essential to establish a consistent bedtime routine. Tips for better sleep include:
- Avoiding screens before bedtime
- Maintaining a dark and quiet sleeping environment
- Practicing relaxation techniques before bed
5. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a critical role in stress management. Consuming a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and antioxidants supports brain function and reduces stress.
6. Seek Professional Help
For severe stress-related issues, therapy and counseling provide structured approaches to managing emotions. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns.
7. Build Strong Social Connections
Having a supportive social circle reduces stress by providing emotional validation and assistance. Spending time with friends, family, or support groups fosters resilience against stressors.
Conclusion
Stress is a normal part of life. Understanding what stress is in psychology helps people cope better. It is important to know the types of stress, its causes, and how to manage it. People can improve their mental and physical health. They can do this by using stress-reducing techniques. Living a healthy lifestyle also helps. Additionally, asking for help when needed is important.