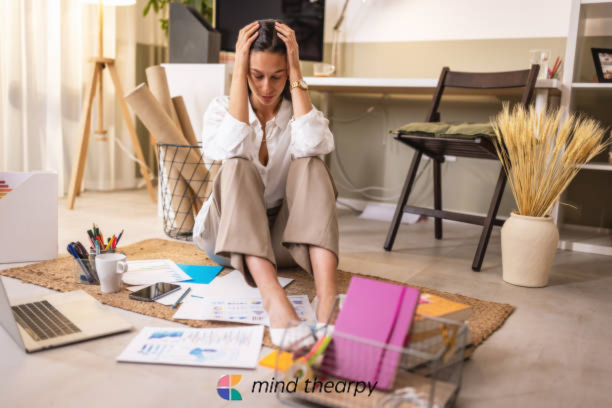
Burnout is a growing concern in today’s fast-paced world, affecting individuals across various professions and lifestyles. Burnout is more than just feeling tired or stressed. It is a state of ongoing physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion. This can greatly affect a person’s well-being. In this article, we will look at the definition of burnout in psychology and healthcare. We will discuss symptoms, causes, treatments, and ways to recover effectively.
Definition of Burnout in Psychology
In psychology, burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion. Long-term and excessive stress can cause this. It often comes from being in stressful situations for too long without enough time to rest and recover. Psychologists describe burnout as a three-dimensional syndrome that includes:
- Emotional exhaustion – Feeling drained, overwhelmed, and emotionally depleted.
- Depersonalization – A sense of detachment from work, colleagues, or responsibilities.
- Reduced personal accomplishment – A decline in motivation, confidence, and effectiveness.
According to Dr. Christina Maslach, a leading researcher on burnout, “Burnout is a psychological syndrome emerging as a prolonged response to chronic interpersonal stressors on the job.”
Definition of Burnout in Healthcare
Healthcare professionals are particularly vulnerable to burnout due to the high-stress nature of their work. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes burnout as an “occupational phenomenon” and categorizes it under work-related stress.
Burnout in Healthcare Workers
- Physicians and nurses experience high emotional exhaustion and depersonalization due to long hours and patient demands.
- Medical students and residents face pressure from heavy workloads, leading to mental health issues.
- Caregivers and mental health professionals often absorb the emotional distress of their patients, increasing their risk of burnout.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that more than 50% of physicians experience burnout symptoms, leading to higher rates of errors, reduced patient satisfaction, and increased physician turnover.
Burnout Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of burnout is crucial for early intervention. The most common signs of burnout include:
1. Physical Symptoms
- Chronic fatigue and lack of energy
- Frequent headaches or muscle pain
- Insomnia or disturbed sleep patterns
- Weakened immune system leading to frequent illnesses
2. Emotional Symptoms
- Feeling detached or cynical about work
- Persistent feelings of helplessness and frustration
- Loss of motivation and enthusiasm
- Increased irritability and mood swings
3. Cognitive Symptoms
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Forgetfulness and decreased productivity
- Constant self-doubt and negative thinking
4. Behavioral Symptoms
- Withdrawal from responsibilities or social interactions
- Procrastination and avoidance of tasks
- Increased reliance on alcohol, caffeine, or other substances
If left untreated, burnout can contribute to anxiety, depression, and severe mental health disorders.
Causes of Burnout
Understanding the root causes of burnout can help prevent and manage it effectively. The most common factors leading to burnout include:
1. Work-Related Causes
- Excessive workload and unrealistic deadlines
- Lack of control over work tasks and responsibilities
- Unclear job expectations and poor communication
- High-pressure work environments with no work-life balance
2. Personal and Lifestyle Causes
- Neglecting personal needs due to professional obligations
- Lack of proper rest, exercise, and nutrition
- Perfectionism and fear of failure
- Limited social support and personal relationships
3. Emotional and Psychological Causes
- Long-term exposure to stressful situations
- Unresolved trauma or past experiences
- Feeling undervalued or unappreciated
- Compassion fatigue, especially in caregiving professions
Burnout Treatment: How to Recover from Burnout
Overcoming burnout requires a holistic approach that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of recovery. Here are some proven strategies to recover from burnout effectively:
1. Prioritize Self-Care
- Ensure adequate sleep and proper nutrition to restore energy levels.
- Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress hormones.
- Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques such as meditation and deep breathing.
2. Establish Work-Life Balance
- Set clear boundaries between work and personal life.
- Take regular breaks during work to avoid mental fatigue.
- Learn to say no to excessive responsibilities and commitments.
3. Seek Social Support
- Talk to friends, family, or professional counselors about stress and emotions.
- Join support groups or online communities to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Develop healthy relationships that provide encouragement and understanding.
4. Make Adjustments at Work
- Communicate with managers or supervisors about workload concerns.
- Delegate tasks to avoid overburdening yourself.
- Explore flexible work arrangements if possible.
5. Engage in Professional Help
- Therapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), can help reframe negative thought patterns.
- Consulting with a mental health professional can provide personalized guidance and strategies.
- If necessary, take a temporary break or sabbatical to focus on mental health.
Preventing Burnout: Long-Term Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some effective ways to prevent burnout in the long run:
- Practice Time Management: Use productivity techniques like the Pomodoro method to work efficiently.
- Engage in Regular Hobbies: Activities like reading, painting, or music help relieve stress.
- Stay Physically Active: Exercise boosts endorphins and enhances overall mood.
- Develop Emotional Resilience: Cultivate a positive mindset and adapt to stress more effectively.
- Take Regular Vacations: Periodic breaks rejuvenate the mind and body.
Conclusion
Burnout is a serious issue that affects millions worldwide, impacting both mental and physical well-being. By recognizing burnout symptoms, understanding its causes, and adopting effective treatment strategies, individuals can regain balance and prevent long-term consequences.