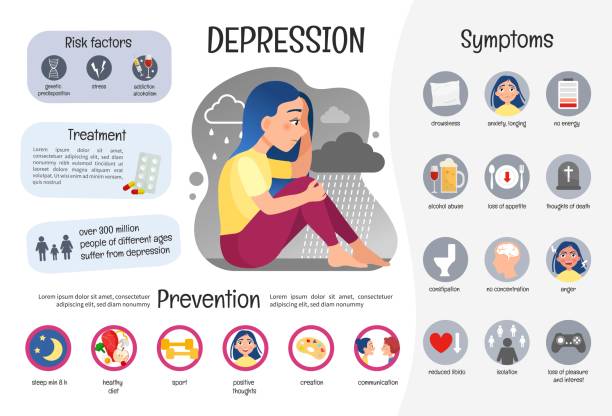
Depression, an important mental health issue, affects millions of people globally. With medical and adjustment for one’s lifestyle, which are important for the management of depression, drugs can also be very effective in reducing symptoms. This article engages in various types of depression drugs, how well they work, and what to think when choosing the most appropriate treatment.
Understanding Depression and Medication Treatment
Feeling below is one thing, but depression is a whole different ball game. This is a real medical condition that throws a wrench in your mood, energy, sleep, and even day-to-day routine. Being better means talking to a physician, taking medicine, or both.
How Do Depression Medications Work?
Drugs of depression help by restoring brain chemicals as a neurotransmitter, such as serotonin, dopamine and noorpenephrine. These chemicals play a big role of how we feel and regulate our feelings, and when they are out of strange, it can cause depression.
Types of Depression Medications
Many types of depression drugs are available. A healthcare professional will determine which is the best based on the person’s symptoms, medical history and reaction to treatment.
1. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are the most prescribed depression drugs. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain and by improving mood and emotional stability.
Common SSRIs:
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Citalopram (Celexa)
Pros:
- Fewer side effects than older antidepressants
- Generally safe for long-term use
Cons:
- May take several weeks to work
- Possible side effects like nausea, headache, and sexual dysfunction
2. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs work by increasing both serotonin and norepinephrine levels. They are useful for individuals who do not respond well to SSRIs.
Common SNRIs:
- Venlafaxine (Effexor XR)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)
Pros:
- Effective for both depression and anxiety
- Helps with nerve pain conditions
Cons:
- May cause increased blood pressure
- Can lead to withdrawal symptoms if stopped suddenly
3. Atypical Antidepressants
These medications do not fit into other categories but are still effective for treating depression.
Examples:
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin) – Works on dopamine and norepinephrine and has fewer sexual side effects
- Mirtazapine (Remeron) – Helps with sleep and appetite loss
Pros:
- Alternative for those who do not tolerate SSRIs or SNRIs
- Some may have fewer side effects
Cons:
- May cause drowsiness or weight gain
4. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
TCAs are older depression medications that are still used in cases where newer treatments are ineffective.
Common TCAs:
- Amitriptyline (Elavil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
Pros:
- Effective for severe depression
- Can help with nerve pain
Cons:
- More side effects than SSRIs or SNRIs
- Can be dangerous in overdose situations
5. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are another older class of antidepressants that are usually prescribed when other medications have failed.
Common MAOIs:
- Phenelzine (Nardil)
- Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
Pros:
- Can be effective for people with treatment-resistant depression
Cons:
- Require dietary restrictions
- Risk of serious side effects when combined with certain foods or medications
Depression Medication List
Here is a summarized depression medication list categorized by type:
- SSRIs: Fluoxetine, Sertraline, Escitalopram, Paroxetine, Citalopram
- SNRIs: Venlafaxine, Duloxetine, Desvenlafaxine
- Atypical Antidepressants: Bupropion, Mirtazapine
- TCAs: Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline, Imipramine
- MAOIs: Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine
Anxiety and Depression Medication
Many antidepressants also work well for treating anxiety disorders.
Best Anxiety and Depression Medications:
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Venlafaxine (Effexor XR)
Postpartum Depression Medication
Postpartum depression affects new mothers after childbirth. The following medications can help:
- Brexanolone (Zulresso) – A unique treatment specifically for postpartum depression
- SSRIs and SNRIs – Often prescribed for long-term management
Best Depression Medication: Choosing the Right One
The best depression medication varies by individual. Some factors to consider include:
- Symptoms: Different medications target different symptoms.
- Side Effects: Some medications cause drowsiness, while others may cause weight gain.
- Other Health Conditions: A doctor will consider any pre-existing medical conditions.
Expert Insights
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) (nimh.nih.gov), the combination of the drug with therapy often provides the best results for people with depression.
A psychiatrist of Psych Central, Dr. John Smith insisted: “It takes time and patience to find the right medicine. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.” (psychcentral.com)
Conclusion
Depression medicines are an essential treatment option for many people who suffer from depression and anxiety. With different types of available, it is important to work with the healthcare provider to find the most appropriate medicine. With changes in therapy and lifestyle, drug can significantly improve symptoms and overall well -being.